Introduction
Item groups are used to categorize and manage item types in the system. They allow you to define common settings, default values, and predefined behaviors for items within each group, streamlining inventory and order management. Item groups help ensure consistency by applying the same properties and configurations to multiple items at once, based on their classification.
When you add an item group, either by clicking the Create New button from the item group list or the + button on the Item Group Details form, the Item Group Details form will open. The fields, sections, and settings within the form may vary based on your system’s configuration and the values selected in other fields.
Item groups can also be accessed and edited by clicking on the item group cell data in various locations throughout the system (e.g., in inventory, job items, invoices). This will open the corresponding Item Group Details form, where you can view or modify the item group settings.
Even though some settings and values are defined at the item group level, further customization can be made at the item type level for certain configurations. However, this is not true for all settings. For example, the Measure Unit Groups must be set at the group level, and while a default value from that group can be defined, the unit group itself cannot be modified at the item type level—only the specific measure unit can be adjusted for individual item types. Additionally, Custom Attributes are set at the group level and are inherited by all item types within that group. The custom attribute list cannot differ between item types that belong to the same item group.
Elements and Their Roles
Main Info Section
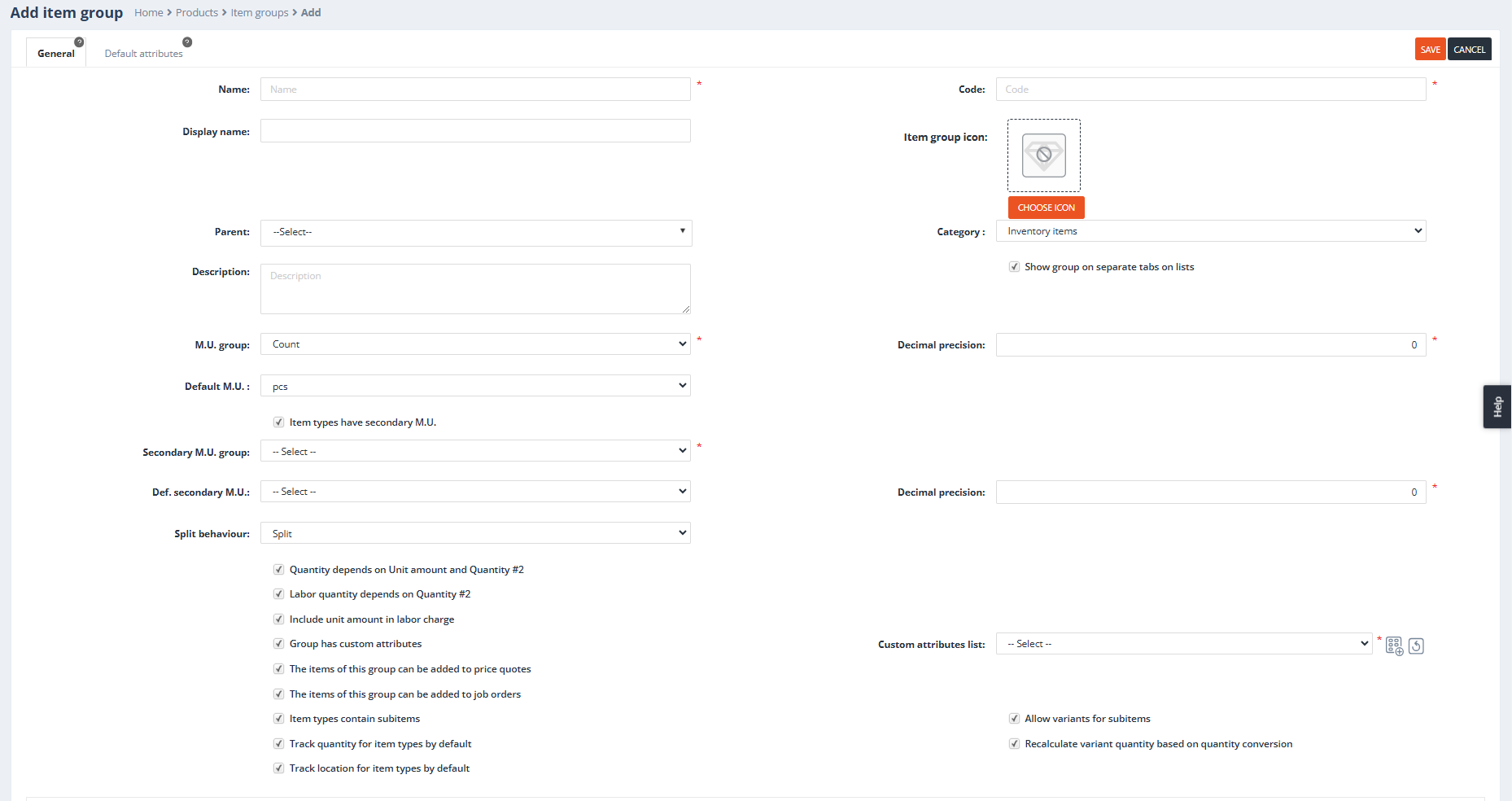
Name
Purpose: Specifies the name of the item group, which is used throughout the system to identify and reference the group.
Behavior:
- The name can be duplicated across different groups but should clearly convey the group’s purpose.
Code
Purpose: Serves as the unique identifier for the item group.
Behavior:
- The system auto-generates this field based on the Name, but it can be manually edited.
- Unlike the name, the Code must be unique across all item groups.
Example:
- Name: Gold Chains → Auto-Generated Code: GOLDCHAINS.
Display Name
Purpose: Used for concise or alternate representation of the item group in system interfaces where space is limited.
Behavior:
- If left blank, the Name will be displayed by default.
- Useful when the Name is too long or complex for streamlined displays.
Parent
Purpose: Specifies a parent item group to organize this group hierarchically.
Behavior:
- Hierarchical structures improve navigation and categorization by allowing subgroups.
- For example, an Earrings group can be a subgroup under a parent group like Jewelry.
Category
Purpose:
Classifies the item group as either Inventory Items or Labor Charges, influencing how the system handles pricing, costing, and usage.
Behavior:
- Inventory Items:
Standard inventory management functionality, including stock tracking, sales, etc. These items are treated as physical products that can be managed and tracked in the inventory system. - Labor Charges:
Special handling for labor-related items, such as repair, stone settings, or other customization services. When the Labor Charges category is selected, the item types within that group can be used as labor services in other inventory item types. These labor items can be assigned to job items, set at the item type level, or configured anywhere labor charges can be applied.
Example:
- Selecting Labor Charges classifies the item types as services (e.g., repair or customization) rather than physical inventory products. These labor charges can then be applied to other inventory items, such as adding labor costs to the price of a product or job.
Description
Purpose: A free-text field for internal notes or explanations about the item group’s purpose or characteristics.
Behavior:
- Visible only to system users.
- Useful for clarifying the group’s usage or special considerations.
Show group on separate tabs on lists
Purpose: If enabled, displays the item group as its own tab in forms such as the inventory list or item type details.
Behavior:
- Enhances visibility and accessibility by isolating the group’s items for quicker management.
Example:
- Enabling this for a group like Jewelry creates a dedicated tab in inventory screens for related items.
Measure Unit Group (M.U. Group)
Purpose: Specifies the measurement unit group (e.g., Weight, Count, Length ) applicable to items in the group.
Behavior:
- Enforces standardized unit definitions for all items.
- Examples: A group for gold items might use a Weight unit group, while a group for finished products might use a Count unit group.
Decimal Precision
Purpose: Defines the number of decimal places for the primary measurement unit when recording item quantities.
Behavior:
- Critical for accuracy, especially for small or high-value items.
- Applies to all item types under the group.
Example:
- Decimal Precision: 3 → Quantities like 1.567 grams are accepted.
- Decimal Precision: 0 → for finished jewelry products (or for M.U.: pcs)
Note:
If the group has a Secondary M.U. Group, a separate precision setting will be available for the secondary unit.
Default M.U.
Purpose: Pre-selects the default measurement unit for items in the group, streamlining item creation.
Behavior:
- The default can be overridden at the item type level.
Example:
- A group for loose diamonds might default to Carats (ct).
- A group for finished rings might default to Pieces (pcs)
Item Types Have Secondary M.U. Group
Purpose: Enables the use of a secondary measurement unit for dual-unit tracking (e.g., Weight and Count).
Behavior:
- Adds additional fields for defining and tracking a second unit group.
- Common for items like gemstones and diamonds, which require dual measures (e.g., Carats for weight and Pieces for count).
Secondary M.U. Group
Purpose: Specifies the measurement unit group for the secondary unit, if enabled.
Behavior:
- Can differ from the primary M.U. group.
Example:
- A jewelry group might use Count as the primary unit and Weight as the secondary unit.
- A diamond group might use Weight (with ct) as the primary unit and Count (pcs) as the secondary unit.
Dependencies:
- This field is visible only if the Item Types Have Secondary M.U. Group checkbox is enabled.
Decimal Precision (Secondary M.U.)
Purpose: Defines the number of decimal places for the secondary measurement unit, ensuring accurate tracking.
Behavior:
- Typically set based on the precision needed for the secondary unit.
Example:
- Decimal Precision: 3 → Quantities like 0.345 carats are supported.
Dependencies:
- Visible only when Item Types Have Secondary M.U. Group is enabled.
Default Secondary M.U.
Purpose: Sets the default secondary measurement unit for the group.
Behavior:
- Simplifies item creation by pre-selecting a secondary unit.
- Example: Default secondary M.U. for a gemstone group could be Carats.
Note:
This field is only accessible if Item Types Have Secondary M.U. Group is enabled.
Split Behavior
Purpose: Determines whether items in this group are subject to splitting into separate child jobs or remain part of the parent job when the Split jobs by parent item types split rule is enabled on services.
Behavior:
- Split:
Items in this group will follow the splitting rules. For example, when multiple items (e.g., a ring and a necklace) are ordered together, they can be split into separate child jobs, ensuring each item is processed independently. - Do Not Split:
Items in this group will bypass splitting, remaining on the parent job. This is useful for scenarios where certain items should not be processed independently, even when splitting rules are active.
Example:
- Use Case:
Orders imported from Shopify contain multiple items, such as a ring and a necklace. With the Split jobs by parent item types split rule enabled, these items will automatically split into separate jobs to ensure independent production workflows for each jewelry piece.
Quantity Depends on Unit Amount and Quantity #2
Purpose: Automates the calculation of the primary quantity based on the product of the Unit Amount and Secondary Quantity (Quantity #2).
Behavior:
- Enable only if Item Types Have Unit Amount and Item Types Have Secondary M.U. Group are also enabled.
- Automatically updates the primary quantity during transactions to reflect changes in either the unit amount or the secondary quantity.
Example:
- A labor group with a unit amount of 5 hours per piece and a secondary quantity of 3 pieces will auto-calculate the primary quantity as 15 hours.
- A diamond – set with primary measure unit as carat and secondary as pcs – with a unit amount of 0.75 and a secondary quantity of 7 pieces will auto-calculate the primary quantity as 5.25 ct
Labor Quantity Depends on Quantity #2
Purpose: Automatically calculates the labor quantity based on the secondary quantity (Quantity #2).
Behavior:
- Applicable only when Item Types Have Secondary M.U. is enabled.
- Reduces manual labor entry by linking labor calculations to the secondary quantity.
Example:
- If the secondary quantity represents pieces and each piece requires 2 hours of labor, the system calculates labor quantity dynamically based on the number of pieces.
Include Unit Amount in Labor Charge
Purpose: Ensures that the Unit Amount is included when calculating labor charges.
Behavior:
- Enabled only when Item Types Have Unit Amount is active.
- Useful for labor-based pricing models, ensuring accurate calculations.
Example:
- If the Unit Amount is 10 dollars per unit and the secondary quantity is 3 units, the labor charge will be 30 dollars.
Group Has Custom Attributes
Purpose: Allows the assignment of custom attributes to the item group, enabling detailed characterization of items.
Behavior:
- Enables the Custom Attributes List field, where a predefined extra attribute list can be selected.
- Custom attributes could include properties like size, color, or material. – for more info, please check the Custom attributes section
Example:
- A group for Gemstones might use attributes such as Clarity, Cut, and Color from the pre-defined attribute list: Gemstone Attributes.
Custom Attributes List
Purpose: Specifies the list of available custom attributes for item types in the group.
Behavior:
- Enabled only if Group Has Custom Attributes is selected.
- Users can select from predefined lists or create new ones tailored to the item group.
- Will list all the attribute lists with the type of: Item type extra attributes
Example:
- A Rings group might use an attribute list called Ring attributes.
Item Types Contain Subitems
Purpose: Enables item types within the group to include subitems or components.
Behavior:
- Adds a Subitems tab to the Item type detail form, allowing users to specify components.
- Useful for managing assemblies or composite items.
Example:
- A Necklace item might include subitems like Chain and Pendant.
Track Quantity for Item Types by Default
Purpose: Automatically enables quantity tracking for all item types within the group.
Behavior:
- If checked, set the Track Item Quantity option to Yes in the item type detail form by default.
Example:
- A group for Finished Jewelry ensures stock levels are tracked for all items by default.
Track Location for Item Types by Default
Purpose: Enables inventory location tracking for all item types in the group by default.
Behavior:
- If checked, set the Track Inventory Location setting to Yes in the item type detail form.
- Used when there are more than one Company location is defined or when there are more than one Inventory location is enabled
Example:
- A group for Raw Materials ensures inventory is tracked across warehouses.
Allow Variants for Subitems
Purpose: Enables the creation of variants for subitems within item types.
Behavior:
- Allows variations (e.g., different metal colors) for components.
Example:
- A Bracelet item might include subitems like Charms, with variants for Gold and Silver.
Recalculate Variant Quantity Based on Quantity Conversion
Purpose: When conversion rates for metals are set, this setting ensures that any metal added as a subitem to a parent item is automatically assigned all available metal variants based on the relevant conversion rates.
Behavior:
- After defining the conversion rates for metals, whenever a metal is added as a subitem to a parent item, the system will automatically create and assign the corresponding variants based on these rates.
- The variant quantity will be recalculated according to the specified conversion rate, ensuring that inventory and production reflect the appropriate metal type and quantity.
Important Note:
- This setting is configured on the parent item group, not the metal’s item group.
- The admin setting: General settings / Inventory / Item type settings: Auto create variants for metal subitems with conversion rates – must be enabled
Example:
- For instance, when adding a 14k gold metal to a parent item, the system will automatically apply all relevant conversion rates (e.g., converting 14k to 18k gold) and generate the corresponding variants. The quantity for each variant will be recalculated based on the conversion rate, ensuring accurate tracking of materials and quantities.
Item Types Settings
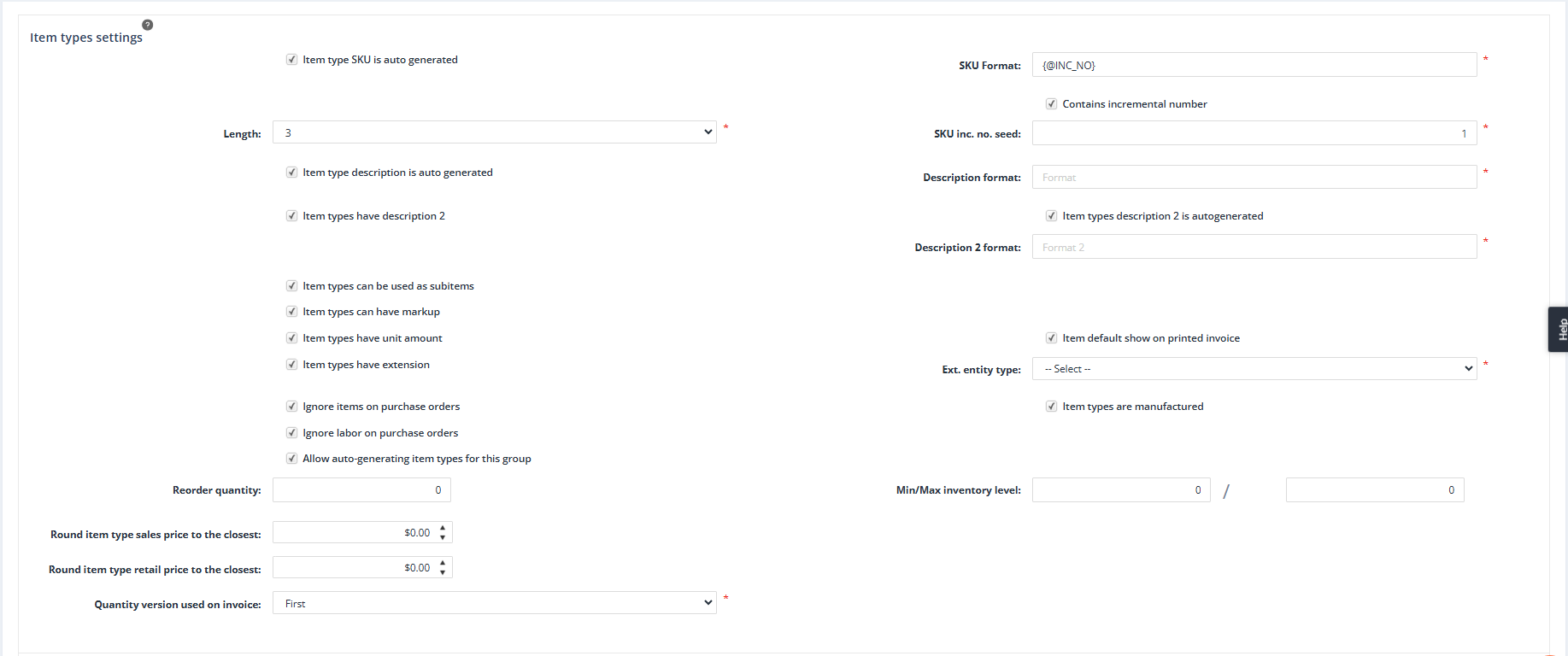
Item Type SKU Is Auto Generated
Purpose: Automatically generates a SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) for each item type in the group. This ensures consistent, unique item type SKUs that follow a predefined format.
Behavior:
- When enabled, manual editing of SKUs will not be possible. The system will use the predefined format to create the SKU.
Note:
If enabled, the SKU Format field will appear and needs to be defined.
SKU Format
Purpose: Defines the pattern used for auto-generating SKUs for items in the group.
Behavior:
- The format typically includes static text and placeholders such as incremental numbers or other item-specific details.
Important note:
- All the usable SKU formats can be found at the: Item SKU and Item Type SKU Auto-Generation Formula Parameters – FAQ:
Dependencies:
- Visible only if Item Type SKU Is Auto Generated is enabled.
Contains Incremental Number
Purpose: Adds an incremental numeric sequence {@INC_NO} to the SKU format to ensure that each item type in the group has a unique identifier.
Dependencies:
- Visible only if Item Type SKU Is Auto Generated is enabled.
- Requires the Length and SKU Incremental Number Seed fields to be defined.
Length
Purpose: Determines the number of digits in the incremental number sequence used for the SKU.
Example: Setting a length of “3” will generate SKUs ranging from 001 to 999.
Dependencies:
- Visible only if Contains Incremental Number is checked.
SKU Incremental Number Seed
Purpose: Sets the starting value for the incremental number sequence. This seed will automatically increase as new item types are created.
Dependencies:
- Visible only if Contains Incremental Number is checked.
Item Type Description Is Auto Generated
Purpose: Automatically generates a description for each item type in the group based on a predefined format.
Dependencies:
- If enabled, the Description Format field will appear and needs to be defined.
Description Format
Purpose: Specifies the pattern used for generating item type descriptions.
Dependencies:
- Visible only if Item Type Description Is Auto Generated is enabled.
Note:
You can find examples in the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) section.
Item Types Have Description 2
Purpose: Adds a secondary description field (Description 2) to the Item Type Details form, providing additional space for item-specific information.
Impact: This allows for more detailed or optional information about the item type to be stored.
Item Types Description 2 Is Auto Generated
Purpose: Automatically generates the secondary description for item types based on a defined format.
Dependencies:
- Visible only if Item Types Have Description 2 is enabled.
- Requires the Description 2 Format field to be defined.
Description 2 Format
Purpose: Defines the pattern for the auto-generated secondary description for item types.
Dependencies:
- Visible only if Item Types Description 2 Is Auto Generated is enabled.
Note:
You can find examples in the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) section.
Item Types Can Be Used as Subitems
Purpose: Determines whether item types in the group can be used as subitems (components) for other item types.
Impact: When enabled, these item types can be added as components or parts to other items.
Example:
- The Raw materials or Components item groups can be added to subitems to Finished jewelry.
Item Types Can Have Markup(?)
Purpose: Allows item types to include markups or discounts in their pricing configuration.
Impact: This flexibility enables pricing adjustments based on specific requirements or conditions.
Item Types Have Unit Amount
Purpose: Enables unit-based tracking for item types, defining the quantity of material or units used per item.
Impact: When enabled, the system will track the quantity of material used for each unit of the item type.
Item Default Show on Printed Invoice
Purpose: Sets the default behavior for whether item types in this group appear on printed invoices.
Impact: If enabled, the “Show item on printed invoice” setting on the Item Type Detail form will also be checked by default.
Item types have extension
Purpose: This setting is used for specific groups (e.g., Master Alloys, Pure Metals, Job Services), and it allows defining the external entity types associated with these groups.
Impact: This helps associate item types with external systems or entities, allowing for better integration and tracking.
Ext. Entity Type
Purpose: This setting is available for specific groups (e.g., Master Alloys, Pure Metals, Job Services), and it defines the external entity types associated with these groups.
Impact: This helps associate item types with external systems or entities, allowing for better integration and tracking.
Dependencies:
- Visible only if Item types have extension is enabled.
Ignore Items on Purchase Orders
Purpose: Prevents item types in the group from being added to purchase orders.
Impact: This setting is typically used for items that are not purchased directly, such as labor or internal components.
Item Types Are Manufactured
Purpose: Indicates that items in this group are manufactured in-house rather than purchased from suppliers.
Impact:
- Differentiates between items that are made internally and those procured externally.
- Commonly used with the Ignore Items on Purchase Orders setting to exclude in-house manufactured items from purchase orders.
- When generating Purchase Orders (POs) from Job Orders (JOs), items with this setting enabled will not appear as options in the Generate Purchase Orders form or on the Required Items on Orders tab.
Ignore Labor on Purchase Orders
Purpose: Excludes labor costs from purchase orders when item types in this group include defined labor charges.
Impact: Ensures that labor is not incorrectly included in purchase order costs for items that involve labor charges.
Allow Auto-Generating Item Types for This Group
Purpose: Allows for the automatic creation of item types for the group based on job orders.
Impact: When enabled, the system can automatically create item types from jobs – the job setting: Create item type on completion – will be checked automatically – streamlining the item creation process.
Reorder Quantity
Purpose: Sets a default reorder quantity for item types in the group.
Impact: This helps automate the purchasing process by ensuring that inventory is replenished when it falls below the defined reorder point.
Min/Max Inventory Level
Purpose: Defines default minimum and maximum inventory levels for item types in the group.
Impact: These settings help manage stock levels by providing automated thresholds for reordering items.
Round Item Type Sales Price to the Closest
Purpose: Rounds the sales price of item types to the nearest specified value for consistency in pricing.
Impact: This helps ensure that pricing remains standardized across all sales transactions, preventing discrepancies due to minor pricing differences.
Round Item Type Retail Price to the Closest
Purpose: Rounds retail prices of item types to the nearest specified value for consistency in retail pricing.
Impact: Similar to sales prices, this ensures retail pricing is consistent and aligned across items.
Quantity Version Used on Invoice
Purpose: If multiple quantity versions exist on the Quantities form (on a Job Order), this setting specifies whether the First or Last version will be used when generating the invoice.
Impact: This ensures that the correct quantity version is reflected on invoices for consistency in billing and reporting.
Inventory Items Settings
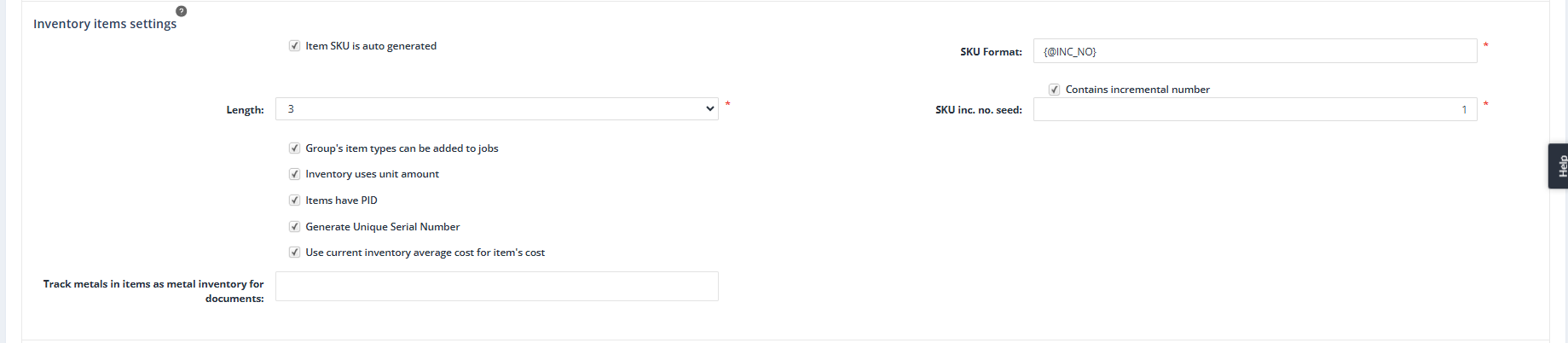
Item SKU Is Auto Generated
Purpose: Automatically generates a unique SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) for each inventory item in this group based on a defined format.
Impact: Ensures that each inventory item has a consistent, unique SKU, preventing duplication.
Dependencies:
- Enables the SKU Format field.
SKU Format
Purpose: Defines the structure and pattern for auto-generating SKUs. This can include static text and placeholders such as incremental numbers or item-specific details.
Dependencies:
- Visible only if Item SKU Is Auto Generated is enabled.
- If Contains Incremental Number is checked, the format will include the placeholder {@INC_NO}.
Note:
You can find examples in the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) section.
Contains Incremental Number
Purpose: Adds an incremental numeric sequence: {@INC_NO} to the SKU Format to ensure each item has a unique SKU.
Dependencies:
- Enables the Length and SKU Incremental Number Seed fields.
Length
Purpose: Specifies the number of digits used for the incremental number in the SKU.
Impact: For example, setting a length of “4” would result in SKUs ranging from 0001 to 9999.
Dependencies:
- Visible only if Contains Incremental Number is checked.
SKU Incremental Number Seed
Purpose: Sets the starting value for the incremental number sequence. The seed automatically increases as new items are created.
Dependencies:
- Visible only if Contains Incremental Number is checked.
Inventory Uses Unit Amount (?)
Purpose: Enables tracking inventory items in terms of units, such as “per gram” or “per piece.” The inventory uses unit amount’ option is used to determine whether the item types from this item group also take into consideration the unit amount when being added to the inventory.
Impact: This setting adds unit-based calculations to inventory tracking, enhancing precision and making it easier to manage items that are measured or sold in variable amounts.
Generate Unique Serial Number
Purpose: Automatically generates a unique serial number for each item in this group.
Impact: This enables detailed tracking and identification of serialized items, improving inventory accuracy and enabling more robust traceability for each unit.
Use Current Inventory Average Cost for Item’s Cost
Purpose: Automatically sets the item’s cost based on the Weighted Average Cost (WAC) of the current inventory, ensuring accurate and real-time cost valuation.
Impact:
- Dynamically reflects the weighted average cost in the item’s cost for documents, improving pricing and financial accuracy.
- Applied when adding the group’s items to most documents – excluding Outgoing Consignment (OC) – or when invoicing a job that includes a service with the code “INVOICING”.
WAC Formula:
WAC = Total Quantity of Inventory / Total Cost of Inventory
Where:
- Total Cost of Inventory: Sum of the costs of all inventory items.
- Total Quantity of Inventory: Total number of inventory items.
Additional Details:
- The WAC calculation ensures that the item’s cost is updated based on inventory movements.
- On the item type level, this calculation can be skipped during invoicing by enabling the “Skip Weighted Average Cost Recalculation During Invoicing” setting, allowing exceptions for specific item types where WAC updates are unnecessary.
Track Metals in Items as Metal Inventory for Documents
Purpose: Enables the system to track and account for metals used in items as part of the inventory, ensuring proper documentation and resource management.
Impact:
- Allows precise tracking of metal usage across selected documents such as Sales Orders, Job Orders, Receipt of Goods, and Invoices.
- Generates a metal inventory movement based on the selected document types, helping to maintain accurate metal stock levels.
- This feature is especially beneficial when there’s a need to track metals separately from finished goods in inventory.
Functionality: This setting uses a multi-selection box, allowing users to specify the documents where metal tracking should be applied.
Example: If this setting is enabled for Receipt of Goods for a Ring group, when a Receipt of Goods (RG) is created for a ring, the system will generate inventory movements for both the ring and its associated metal subitem. This ensures that the metal used in the ring is accurately recorded and accounted for in the inventory.
Services
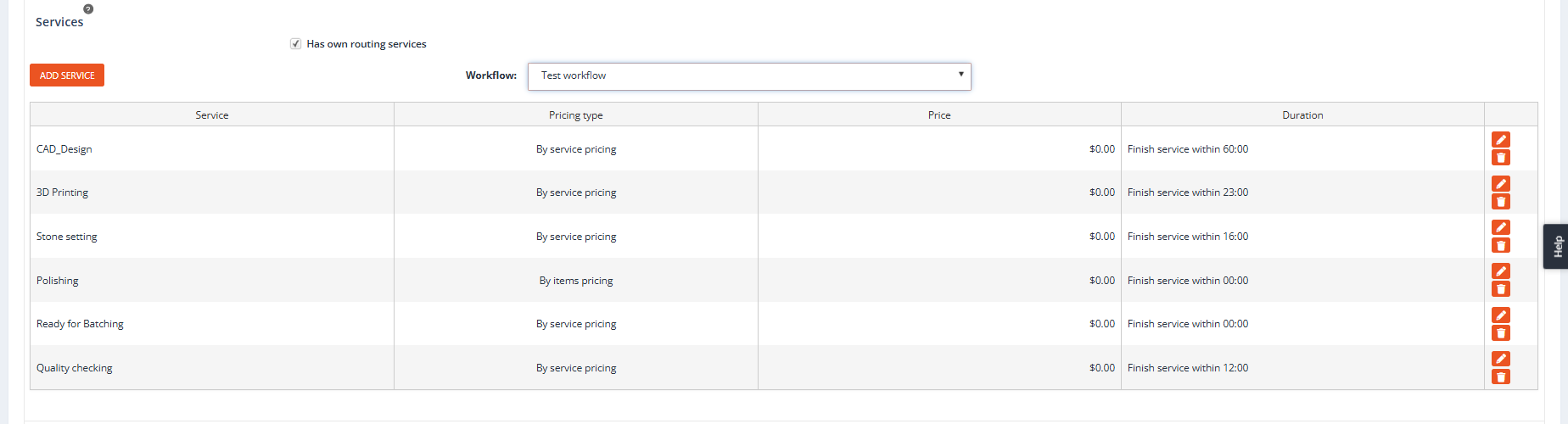
Has Own Routing Services
Purpose: Enables the assignment of workflows or individual services to the item group.
Impact:
- When checked, the Workflow dropdown list and the Add Service button become available.
- Allows users to either select a predefined workflow or manually add individual services to the item group.
Workflow
Purpose: Displays a list of predefined workflows that can be applied to the item group.
Impact:
- Selecting a workflow will automatically add all services associated with it to the group.
Visibility: - Available only if Has Own Routing Services is checked.
Add Service
Purpose: Provides the flexibility to add individual services one by one to the item group.
Functionality:
- Opens the Add Service Type form, where users can specify and add desired services.
- Can be used in conjunction with or as an alternative to selecting a workflow.
Inventory Item Grouping
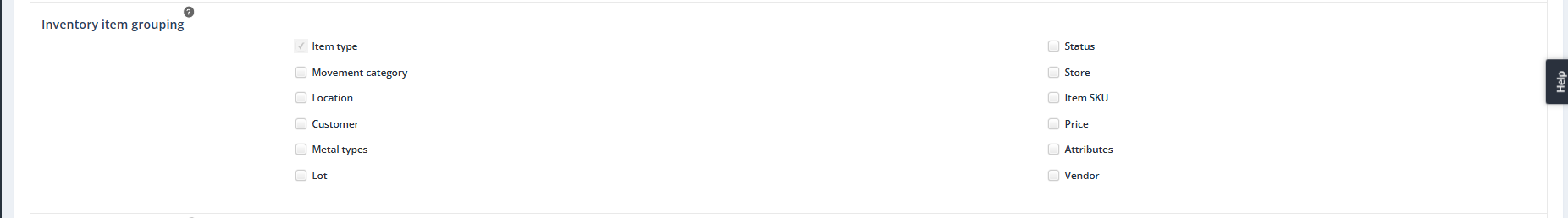
Important Notes:
- Group Display:
Grouping settings affect only aggregated views, such as the Current Inventory form. - Detail View:
The Inventory History form always shows separate inventory movements, regardless of grouping settings.
Grouping Options
Purpose: You can group inventory items by the following criteria:
- Item Type (Default, cannot be changed)
- Movement Category
- Location
- Customer
- Metal Types
- Lot
- Status
- Store
- Item SKU
- Price
- Attributes
- Vendor
Customer Portal Settings

Has Customer Portal Attributes:
Purpose:
- Enable this option to assign custom attributes for the customer portal.
- When checked, it allows customization of the details displayed for items in this group on the customer portal.
Attributes List:
Purpose:
- Select an appropriate attribute list from the available “Portal Category Item Type Attributes” lists.
- This list determines the additional details or specifications shown for items in this group on the customer portal, providing a tailored experience for customers.
Dependencies:
- Visible only if Has Customer Portal Attributes is checked.
Default Attributes Tab
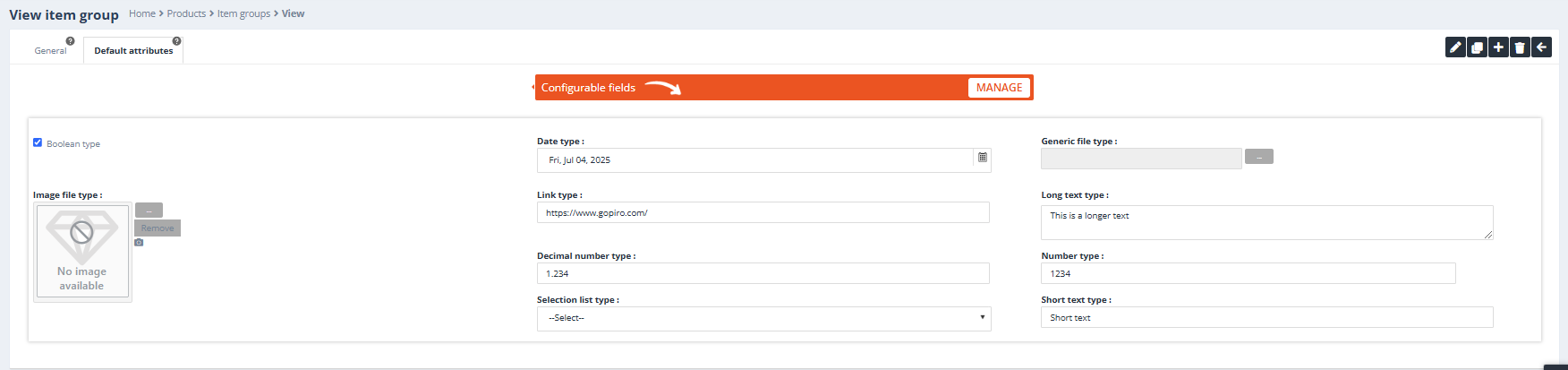
Purpose:
The Default Attributes tab reflects the attributes defined in the currently selected Custom Attributes List. These attributes will be inherited by all item types within the group.
Dependencies:
- Visible only if Group Has Custom Attributes is checked.
Behavior:
- All item types in the group share the same attributes, as defined by the Custom Attributes List.
- Default values can be set on the item type level only.
- Individual item types can have their default values, but the attributes themselves (types) remain consistent across all item types in the group.
Example:
- If the Custom Attributes List includes attributes like Material, Size, and Finish, every item type in the group will have these attributes.
- An individual item type, like a Ring, can define its own default Material to “Silver” while still having the same attributes (Material, Size, Finish).
Buttons:
Action buttons (View mode):

- Edit: Allows editing of the current item group details.
- Copy: Creates a duplicate of the current item group for easy replication.
- Create New: Opens a blank form to create a new item group.
- Delete: Removes the current item group from the system (subject to permissions and dependencies).
- Manage Attribute-Based Prices (optional): Available only for groups with assigned Attribute Lists. Opens the pricing management interface, the Attribute based price List.
- Back: Redirects the user to the item group list page.
Action buttons (Edit mode):

- Save: Saves the changes made to the item group and updates the system.
- Cancel: Discards any unsaved changes and exits edit mode.
- Copy: Creates a duplicate of the current item group for replication.
- Create New: Opens a blank form to create a new item group.
- Delete: Removes the current item group from the system (subject to permissions and dependencies).
- Manage Attribute-Based Prices (optional): Visible only for groups with assigned Attribute Lists. Opens the interface for managing pricing based on attributes.
Icons for Item Groups with Assigned Attribute Lists
Note:
These icons are displayed next to the Custom Attributes List dropdown when the Group Has Custom Attributes checkbox is selected:
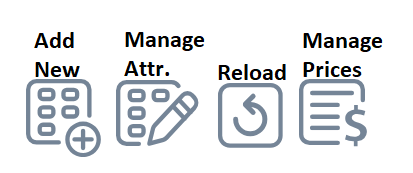
- Add New Attribute List: Opens the “Add Custom Attribute List” form to create a new attribute list.
- Manage Attributes: Opens the selected attribute list to edit or manage its attributes.
- Reload Custom Attributes List: Refreshes the dropdown to display newly created attribute lists if they are not appearing as selectable options.
- Manage Attribute-Based Prices: Opens the “Attribute-Based Price List” form to configure pricing based on attributes.
Item Groups – FAQ
1. What is an Item Group?
Answer:
An item group is a collection of items that share common characteristics or attributes. These items can be categorized based on similar traits such as metal types, product types, or functionality. Item groups are used to organize and manage inventory more efficiently, enabling bulk operations and simplified tracking.
Example:
A jewelry manufacturer may have item groups for “Rings,” “Necklaces,” and “Earrings,” where each group includes items that belong to the respective category. This helps in streamlining inventory and item type management, pricing, and reporting.
2. How does the ‘Item Type SKU Is Auto Generated’ setting work?
Answer:
When enabled, this setting automatically generates a unique SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) for each item type in the group. The generated SKU follows a predefined format and ensures consistency and uniqueness across all items in the group. This setting also prevents manual editing of SKUs.
Example:
For an item group of rings, the SKU could be auto-generated with a format such as “RNG-{@INC_NO}” where {@INC_NO} is a placeholder for an incremental number. The first item will be “RNG-001,” the second “RNG-002,” and so on.
3. What is the purpose of the ‘Contains Incremental Number’ checkbox?
Answer:
When checked, it adds an incremental numeric sequence to the SKU format. This ensures that each item in the group receives a unique identifier.
Example:
In the “Rings” item group, the SKU format could be “RNG-{@INC_NO}”. If “Contains Incremental Number” is enabled, SKUs will be generated starting from “RNG-001” and incrementing for each new item.
4. Can I define a specific starting point for the incremental SKU sequence?
Answer:
Yes, the “SKU Incremental Number Seed” field allows you to set the starting value for the incremental sequence. This ensures that you can control the starting point of the numbering system.
Example:
If you set the seed value to 100, the first SKU will be “RNG-100,” and subsequent SKUs will increment from there (e.g., “RNG-101,” “RNG-102,” etc.).
5. What is the ‘Has Custom Attributes’ checkbox used for?
Answer:
This checkbox enables the assignment of custom attributes to items within the group. Custom attributes can specify additional details like size, color, material, or other product characteristics that are relevant for the item.
Example:
In a “Rings” item group, custom attributes could include “Ring Size,” “Metal Color,” or “Gender.” These attributes allow for more granular tracking and provide extra information for customers or staff.
6. What is the ‘Track Quantity for Item Types by Default’ setting?
Answer:
When checked, this setting automatically enables the “Track Item Quantity” setting for all item types within the group. This ensures that inventory levels for all items in the group are tracked by default.
Example:
If this setting is enabled for the “Rings” group, every new ring item added to the system will have the “Track Item Quantity” option automatically set to “Yes,” meaning inventory levels for rings will be tracked. This can be modified for each item type within this group (on the item type level).
7. How does ‘Allow Variants for Subitems’ impact item groups?
Answer:
When checked, this setting enables the creation of variants for subitems within the group. Variants allow for multiple configurations of a base item, such as different sizes, colors, or materials, and are typically used for items that come in different options.
Example:
For a “Rings” item group, a subitem could be a “Gold Ring.” If “Allow Variants for Subitems” is enabled, you could create variants for different metal types (e.g., 14K Gold, 18K Gold).
8. What is the difference between ‘Group Has Custom Attributes’ and ‘Custom Attributes List’?
Answer:
- Group Has Custom Attributes enables the assignment of custom attributes to an item group.
- Custom Attributes List is where you define which attribute lists can be assigned to the group once custom attributes are enabled.
Example:
If the option “Group Has Custom Attributes” is checked for the “Rings” item group, you can select a custom attribute list, such as “Ring Attributes” or “Jewelry Attributes,” to further define the characteristics of each ring within the group. Please note that both “Ring Attributes” and “Jewelry Attributes” must be created beforehand as custom attribute lists with Item type extra attributes types.
9. What does the ‘Recalculate Variant Quantity Based on Quantity Conversion’ setting do?
Answer:
This setting recalculates the quantity of a variant based on its quantity conversion rate. This is particularly useful when dealing with metals, where the weight or quantity may need to be adjusted when converting between different metal types (e.g., from 14K gold to 18K gold).
Example:
If the variant for a “Gold Ring” is set to 10 grams of 14K gold and the conversion rate to 18K gold is 1.2, the recalculated quantity for the variant would be 12 grams when the metal is changed to 18K gold. This ensures that the proper amount of material is accounted for in inventory and production calculations.
10. Can I group inventory by different criteria?
Answer:
Yes, inventory items can be grouped by various criteria, including:
- Item Type
- Movement Category
- Location
- Customer
- Metal Types
- Lot
- Status
- Store
- Item SKU
- Price
- Attributes
- Vendor
Each of these options helps to organize inventory in ways that make it easier to manage, track, and report.
Example:
- Grouping by Location can help track the items across multiple Compay or Inventory locations.
- Grouping by Item SKU can be used to manage stock levels for the same item type with different SKUs.
11. What happens if I enable ‘Item Types Can Be Used as Subitems’?
Answer:
Enabling this option allows items within the group to be used as subitems for other item types. This is useful when items are components or parts of a larger product.
Example:
If the “Necklaces” item group has an item type for “Necklace Chains,” enabling “Item Types Can Be Used as Subitems” will allow you to add “Necklace Chains” as a component to other items like “Gold Necklaces.”
12. What is the ‘Item Types Are Manufactured’ setting used for?
Answer:
When checked, this setting indicates that items in the group are manufactured rather than purchased. This is particularly useful for managing items that are produced in-house.
Example:
For a “Custom Jewelry” item group, enabling “Item Types Are Manufactured” will signal that all items in the group, such as “Custom Rings” or “Bespoke Bracelets,” are created internally and not purchased from suppliers.
13. What is the ‘Has Own Routing Services’ setting?
Answer:
This option indicates that every item in the group has its own predefined workflow or services. When an item from this group is added to a job order, the system prompts the user to confirm if the group’s default workflow should be applied to the job. These workflows or services can be further adjusted or overridden at the item type level for greater customization.
Example:
For a Ring item group, enabling “Has Own Routing Services” allows you to define a default workflow like:
- Design
- Design Approval
- Casting
- Cleaning
- Stone Setting
- Quality Check
- Invoicing
- Shipping
When a ring item is added to a job order, the system will ask if this workflow should be applied to the job. This ensures that every item from the Ring group follows consistent steps but still provides flexibility to modify services for specific jobs.
Additional notes:
Item SKU and Item Type SKU Auto-Generation Formula Parameters – FAQ:
1. What are the available formula parameters for auto-generating both Item SKUs and Item Type SKUs?
Answer:
The following parameters can be used in the auto-generation formula for both Item SKUs and Item Type SKUs:
- {@INC_NO} – Inserts an automatically incrementing number based on the ‘SKU inc. no. seed’ and ‘Length’ values.
- Example:
ITEM-{@INC_NO}would generate SKUs like “ITEM-001”, “ITEM-002”, etc.
- Example:
- {@IG#C} – Inserts the code of the item group to which the item belongs.
- Example: For the “Rings” item group, if the code is “RG”, the SKU would be “RG-001”, “RG-002”, etc.
- {@IG#N} – Inserts the name of the item group to which the item belongs.
- Example: If the item group is “Rings”, the SKU would be “Rings-001”, “Rings-002”, etc.
- {attribute_code} – Inserts the item’s attribute value (you need to specify the attribute code).
- Example:
{MetalType}might insert “Gold” if the item’s attribute is “Gold”.
- Example:
- {attribute_code}#C – (Selection list attributes only) Inserts the item’s attribute value’s code (label list item’s code).
- Example:
{MetalType#C}could insert the code “GLD” for “Gold” if the attribute is a selection list.
- Example:
- {attribute_code}#D – (Selection list attributes only) Inserts the item’s attribute value’s description (label list item’s description).
- Example:
{MetalType#D}could insert “Gold” as the description of the “Gold” label.
- Example:
- {@SI_IG(subitem’s item group code)#N} – Inserts the name of the item type to which the subitem belongs.
- Example: If the subitem belongs to the item group “Chains”, it could insert “Chains” into the SKU.
- {@SI_IG(subitem’s item group code)[subitem_attribute_code#N]} – Inserts the subitem’s attribute value based on the item group and subitem attribute code.
- Example: If a subitem’s attribute is “Size”,
{Size}could be used to insert the size value.
- Example: If a subitem’s attribute is “Size”,
- {@SI_IG(subitem’s item group code)[subitem_attribute_code#C]} – (Selection list attributes only) Inserts the subitem’s attribute value’s code.
- Example: If the subitem’s “Size” attribute code is “S”, it would insert “S” as part of the SKU.
- {@SI_IT(subitem’s item type code)[subitem_attribute_code#N]} – Inserts the subitem’s attribute value for the specified item type.
- Example: If the subitem type “Ring” has a “Material” attribute, it might insert “Gold”.
- {@SI_IT(subitem’s item type code)[subitem_attribute_code#C]} – (Selection list attributes only) Inserts the subitem’s attribute value’s code.
- Example: If the “Material” attribute is “Gold”,
{Material#C}would insert “GLD”.
- Example: If the “Material” attribute is “Gold”,
2. What are the formula parameters that can only be used for auto-generating Item SKUs?
Answer:
The following parameters are unique to auto-generating Item SKUs:
- {@P_INC_NO} – If the current item group is a subgroup, this formula inserts the incrementing number from the parent item group. This is useful for maintaining consistent numbering across subgroups.
- Example: If the parent group has a seed of 500, this will generate SKUs like “500”, “501”, etc., for the subgroup.
- {@IT#C} – Inserts the code of the item type to which the item belongs.
- Example: If the item type is “Ring”, the SKU will include “RING-001”.
- {@IT#N} – Inserts the name of the item type to which the item belongs.
- Example: If the item type is “Ring”, the SKU might read “Ring-001”.
- {@SI_IG(subitem’s item group code)#C} – Inserts the code of the item type to which the subitem belongs.
- Example: If the subitem belongs to the “Chains” group and its code is “CH”, it might produce “CH-001” as part of the SKU.
- {@SI_IT(subitem’s item type code)#N} – Inserts the name of the item type to which the subitem belongs.
- Example: If the subitem is of item type “Chain”, the SKU might read “Chain-001”.
- {@SI_IT(subitem’s item type code)#C} – Inserts the code of the item type to which the subitem belongs.
- Example: If the subitem is a “Gold Ring” with a code “GR”, the SKU would be “GR-001”.
- {@SI_IG(subitem’s item group code)[subitem_attribute_code#D]} – (Selection list attributes only) Inserts the subitem’s attribute value’s description.
- Example: If the subitem’s attribute “Material” is “Gold” and the description is used, the SKU might be “Gold-001”.
- {@SI_IT(subitem’s item type code)[subitem_attribute_code#D]} – (Selection list attributes only) Inserts the subitem’s attribute value’s description.
- Example: If the “Size” attribute of the subitem is “Small”, it might insert “Small” into the SKU.
- {@SIS_IG(subitem’s parent item group code)[#C]} – Inserts the code sequence of the item types to which the subitems belong.
- Example: If the subitem belongs to “Rings” (code “R”), it will insert “R-001” into the SKU.
- {@SIS_IG(subitem’s parent item group code)[#CQ]} – Inserts the quantity and code sequence of the item types to which the subitems belong.
- Example: If there are 10 subitems with code “R”, it would display “R-10” in the SKU.
- {@SIS_IG(subitem’s parent item group code)[#N]} – Inserts the name sequence of the item types to which the subitems belong.
- Example: If the parent item group is “Rings” and it contains “Gold”, the SKU will show “Rings-Gold”.
- {@SIS_IG(subitem’s parent item group code)[#NQ]} – Inserts the quantity and name sequence of the item types to which the subitems belong.
- Example: If the parent item group is “Necklaces” and there are 5 subitems, it could read “Necklaces-5”.
3. How do I create an example SKU with these parameters?
Answer:
Let’s say you are creating an SKU for a “Gold Ring” in the “Rings” item group with the following specifications:
- Incremental number (starting at 001)
- Metal Type attribute set to “Gold”
- Item type code “RNG”
- Subitem “Gold Ring” with a “Material” attribute of “Gold”.
You might create an SKU like this:
RNG-{@INC_NO}-{MetalType#C}-{Size}
This would generate a SKU like:
“RNG-001-GLD-Small”
Where:
- “RNG” is the item type code
- {@INC_NO} generates a unique number for each item
- “{MetalType#C}” inserts “GLD” for the “Gold” material
- “{Size}” inserts the size (e.g., “Small”).
This allows for dynamic generation of item-specific SKUs based on their attributes and groupings.
4. How do I modify the SKU format to include subitem details?
Answer:
To include subitem details in the SKU, you can use parameters like {@SI_IT(subitem’s item type code)[subitem_attribute_code#N]}.
For example, if you want the SKU for a “Gold Ring” that includes the size of the subitem, you could use this format:
RNG-{@INC_NO}-{@SI_IT(subitem’s item type code)[Size]}
This would generate a SKU like:
“RNG-001-Small” for a small-sized Gold Ring.
This allows SKUs to be generated with subitem-specific attributes, ensuring unique identification based on both parent and subitem characteristics.
Item Group Auto-Generation Formula Parameters – FAQ
1. What formula parameters can be used for auto-generating Item Group settings?
Answer:
You can use the following parameters to auto-generate Item Group settings:
- {@INC_NO} – Inserts an automatically incrementing number based on the seed value.
- Example: If the seed value starts at 100, the result will be “100”, “101”, etc.
- {@P_INC_NO} – Inserts the group inherited seed from the parent group, if applicable. Useful for maintaining a consistent numbering sequence across subgroups.
- Example: If the parent group seed is 500, the generated number will follow that sequence.
- {INI_COLOR} – Inserts the selected color attribute for an item. If no color is defined, it is replaced with an empty string.
- Example: If the item has the color “Red” defined,
{INI_COLOR}would be replaced with “Red”. If no color is set, it would be replaced with an empty string (e.g., “Red” or “”).
- Example: If the item has the color “Red” defined,
- {INI_CT} – Inserts the selected carat attribute for a style. If the carat is defined (e.g., “1.5ct”), it will be inserted. If not, it will be empty.
- Example: If the item’s carat is “1.5ct”,
{INI_CT}will be replaced with “1.5”.
- Example: If the item’s carat is “1.5ct”,
- {@IG#C} – Inserts the code of the item group in which the current item type is located.
- Example: If the item group code is “RNG” (for rings), the SKU would include “RNG”.
- {@IG#N} – Inserts the name of the item group in which the current item type is located.
- Example: If the item group name is “Rings”, the SKU would include “Rings”.
- {@SI_IG(MASTER_ALLOY)#C} – Inserts the code of the subitem’s group which belongs to the “MASTER_ALLOY” group.
- Example: If the subitem group “MASTER_ALLOY” has the code “MA”, it will insert “MA”.
- {@SI_IG(MASTER_ALLOY)#N} – Inserts the name of the subitem’s group which belongs to the “MASTER_ALLOY” group.
- Example: If the subitem group “MASTER_ALLOY” is named “Alloy”, it will insert “Alloy”.
- {@SI_IT(LALA)#C} – Inserts the code of the subitem which is an “LALA” item type.
- Example: If the item type “LALA” has the code “LAL”, it will insert “LAL”.
- {@SI_IT(LALA)#N} – Inserts the name of the subitem which is an “LALA” item type.
- Example: If the item type “LALA” is named “Large”, it will insert “Large”.
- {@SI_IT(DIA1)[INI_COLOR]} – Inserts the color attribute for a subitem type with the code “DIA1”.
- Example: If the “DIA1” subitem has a color attribute set to “Blue”, this would insert “Blue”.
- {@SI_IG(DIA1)[INI_COLOR]} – Inserts the color attribute for a subitem type within the “DIA1” item group.
- Example: If the “DIA1” item group has a color attribute of “Blue”, this would insert “Blue”.
- {STONE TYPE#C} – Inserts the code, name, or description for the stone type, depending on whether
C(Code),N(Name), orD(Description) is used.- Example: If the stone type code is “S” (for sapphire), using
{STONE TYPE#C}would insert “S”.
- Example: If the stone type code is “S” (for sapphire), using
2. Can you provide examples of how these formula parameters would be used?
Answer:
Here are some examples of how these formula parameters might be used to auto-generate SKUs and item settings:
{@INC_NO}; OWNC-{INI_CT}{INI_COLOR}; G-{@IG#C}; SI:{@SI_IG(STYLE)#N}- Explanation: This formula combines several elements:
{@INC_NO}– Generates an incremental number for the SKU.OWNC-{INI_CT}{INI_COLOR}– Includes the carat ({INI_CT}) and color ({INI_COLOR}) of the item.G-{@IG#C}– Includes the group code ({@IG#C}) for the item.SI:{@SI_IG(STYLE)#N}– Includes the name of the subitem group associated with the “STYLE” item group.
- Example Output:
100; OWNC-1.5ctRed; G-RNG; SI:STYLE
- Explanation: This formula combines several elements:
{@SI_SP(Centre)[STONE SHAPE#N]}- Explanation: This formula generates the stone shape for the subitem in the “Centre” position.
- Example Output: If the stone shape is “Round”, the result would be
Round.
{@SI_SP(Side)[STONE SHAPE#N]}- Explanation: Similar to the previous example, this formula generates the stone shape for the subitem in the “Side” position.
- Example Output: If the stone shape is “Oval”, the result would be
Oval.
{@SI_SP(Centre)[NUMBER]}- Explanation: This formula generates the number of stones in the “Centre” position.
- Example Output: If there are “3” stones in the centre, the result would be
3.
{@SI_SP(Side)[STONE COLOUR#N]+}- Explanation: This formula generates the stone color for the subitem in the “Side” position.
- Example Output: If the stone color is “Blue”, the result would be
Blue.
3. How do I handle attributes that might not be defined?
Answer:
When using attributes that may not be defined for a specific item, such as {INI_COLOR}, the system will insert an empty string if the attribute is not set. For example:
{INI_COLOR}– If the “Color” attribute is not defined for the item, this will be replaced with an empty string (e.g., “Red” or “”).
This behavior ensures that your SKU or group generation remains consistent even if some attributes are not defined for every item.
